Looking to future-proof your business with cloud service models but unsure which would best suit your company’s needs?
If so, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered.
In this blog, we help you ascertain the key features of different cloud service models, weigh the pros and cons of each, and introduce you to industry leaders who can make your cloud journey feel like a breeze.
So, buckle up and read on to make the right pick!
What are Cloud Service Models?
Planning to launch an application or create a custom software solution? Imagine not having to worry about the hardware or deal with the complexities of server maintenance.
Well, that’s exactly what cloud service models offer, leveling the playing field for both startups and established brands alike.
They provide companies with flexible, scalable, and affordable solutions to innovate, reduce overhead, and adapt to fluctuating workloads, without having to invest in expensive infrastructure.

Looking to embrace the cloud? Read our detailed blog on cloud migration and drive innovation for your brand.
Types of Cloud Service Models
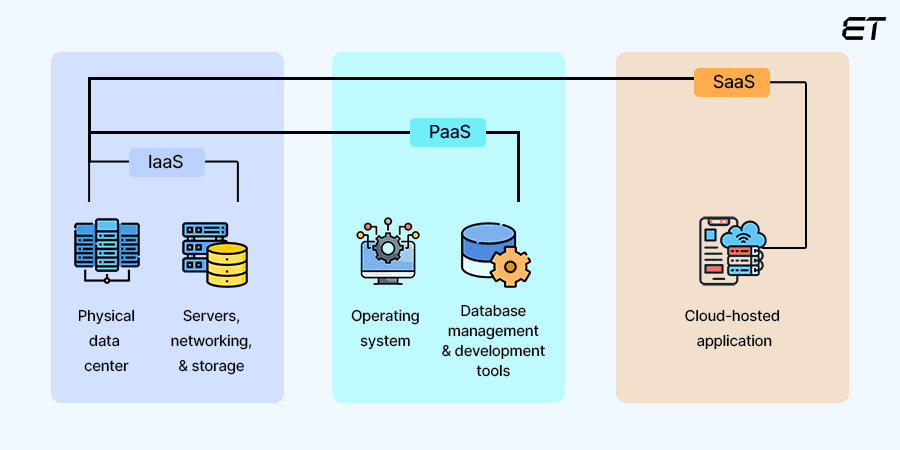
There are three main types of cloud service models— IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS— each offering unique benefits that help with different business needs. Let’s understand this better.
Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS, also known as Hardware as a Service (HaaS), is a cloud service model that delivers computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems, on an outsourced basis. This helps businesses scale up or down based on fluctuating demands without investing in physical hardware.
How Does IaaS Work?
IaaS operates by abstracting physical servers into isolated virtual machines, using advanced hypervisors. These machines can be deployed, scaled, and configured via an API or web interface. Its various components— networking, storage, and computation resources— are all handled by automated processes, facilitating scalability and quick implementation. IaaS cloud service models also offer extensive security features, such as VPNs and firewalls, to safeguard data.
When to Choose IaaS?
If your company needs scalable and adaptable IT infrastructure without the upfront expenses and hassles of managing physical infrastructure, opt for IaaS cloud service models. It is the ideal fit if your business needs immediate performance boosts. Startups and growing brands that require rapid provisioning and scalability to effectively manage changing and unpredictable workloads, find IaaS a viable option. Its pay-as-you-go model allows them to optimize costs by only paying for what they use.
Since it allows rapid resource deployment, it particularly works well for development and testing setups where agility is essential. Businesses looking to improve their disaster recovery capabilities might also find IaaS useful for reliable backup and recovery services.
IaaS also becomes the better option for businesses seeking operational flexibility.
Benefits and Limitations
IaaS cloud service models have the following benefits and limitations that you must consider.
| Pros | Cons |
| Reduced cost: Businesses need not pay large upfront investment in physical hardware. They only pay for the resources they use. | Limited authority over infrastructure: Since IaaS providers manage infrastructure, maintenance, and updates, businesses have limited control, making customization difficult. |
| Scalability and flexibility: Enterprises can easily scale resources up or down based on workload fluctuations, ensuring cost savings during periods of low usage and optimal performance in peak hours. | Vendor lock-in: Platform-specific services and APIs make shifting workloads across multiple IaaS providers challenging, creating reliance on a single provider. |
| Disaster recovery: Built-in encryption, backup, and recovery solutions guarantee data integrity and business continuity. | Compliance issues: Ensuring compliance with industry-specific standards becomes tricky, especially when data is housed across multiple geographical locations. |
|
Global operations: Facilitates geographical scalability by deploying machines closer to end-users to reduce latency, which in turn improves user experience. |
|
|
Swift rollout: It accelerates development and deployment cycles by rapidly allocating and releasing resources. |
Leading IaaS Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS): Provides an extensive range of services such as EC2 for processing, S3 for storing, and VPC for networking.
Microsoft Azure: It is a suite of tools that facilitates the migration and modernization of on-premises infrastructure, data, schema, and applications to the Azure cloud. It offers a variety of IaaS solutions such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage, and more.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Its Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Virtual Network IaaS services make it an industry leader.
IBM Cloud: Has made a name for its secure and scalable IaaS solutions, with a special focus on hybrid cloud environments and enterprise applications.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI): With state-of-the-art computing and storage solutions, it is known to focus on performance-intensive applications.
Some other market leaders include DigitalOcean, Linode, Rackspace, and Cisco Metacloud.
Platform as a Service
PaaS as a cloud service model offers a full development and deployment environment. It allows developers to create, test, launch, manage, and update apps without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. This simplifies the entire app development lifecycle.
It encompasses everything— infrastructure (storage, network, servers), development tools, business intelligence services, database management systems, security solutions, and an easy-to-use graphic user interface (GUI).
How Does PaaS Work?
PaaS cloud service models give developers a platform to manage and abstract the infrastructure, freeing them up to focus on the application layer. It includes virtual servers, networking, and storage solutions, as well as middleware and runtime environments for different programming languages.
They guarantee high availability and optimal performance, offering load balancing, automatic resource scaling, and continuous monitoring. Additionally, it incorporates cutting-edge services like pipelines for continuous integration and deployment, identity and access management, and database handling, which accelerates time-to-market considerably.
When to Choose PaaS?
If your company primarily seeks speedy development and deployment, choose PaaS as it can allow you to concentrate on coding instead of worrying about the complexities of infrastructure management. Since PaaS cloud service models automate load balancing and resource scaling, it’s also the go-to option for companies desiring scalability.
Additionally, its integrated capabilities for team collaboration and version control, make it the ideal choice for collaborative development environments.
If your company has to create apps for several platforms or quickly prototype and iterate, PaaS provides the necessary flexibility and built-in services that minimize operational overhead, while fast-tracking the process.
Benefits and Limitations
Like most cloud service models, PaaS offers several benefits, but not without its fair share of disadvantages. Let’s consider them.
| Pros | Cons |
| Accelerates time-to-market: Its ready-to-use tools and services speed up the development process and allow quicker product launches. | Safeguarding of data: Your business has limited control over data as PaaS providers tend to have data ownership regulations and policies. |
| Supports multi-platform development: It is compatible with varied platforms such as web, mobile, and IoT, offering a unified environment for varied requirements. | Limited customization: They may not provide the degree of customization needed by some applications, especially for configuring middleware or the underlying infrastructure. |
|
Fosters collaboration: PaaS streamlines collaboration among distributed development teams, designers, and stakeholders by providing a centralized environment. |
Vendor lock-in: Since PaaS providers have platform-specific services, APIs, and customizations, moving apps and data between them often proves tricky, resulting in vendor dependency. |
|
Integrated development and security tools: They offer a range of development tools such as integrated development environments and version control systems. They also bear robust security features like data encryption and access controls. |
|
|
Reduces management overhead: A PaaS provider relieves IT teams of the operational load by managing system maintenance, which includes implementing patches, running updates, and upgrading hardware. |
Leading PaaS Providers
Google App Engine (GAE): It provides a fully managed, user-friendly system that supports various programming frameworks like Python, Java, Node.js, and PHP. It also boasts numerous applications with integrated monitoring and automatic scaling tools.
Microsoft Azure: It integrates with other Azure services like GitHub, Bitbucket, and AzureDevOps for effortless deployment. It stands tall in the industry also for its high standard of compliance and built-in security solutions.
Heroku: It supports several programming languages and is hence renowned for its developer-friendly environment. There is also a marketplace for third-party add-ons, facilitating flexibility and customization.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: It integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like CloudWatch, S3, and RDS, allowing customization and automatic resource management. Not to forget, it comes with built-in AWS disaster recovery.
IBM Cloud Foundry: It is an open-source PaaS cloud service model that offers flexibility, allowing businesses to avoid vendor lock-in. It comes with robust tools for automatic testing and continuous delivery.
Force.com, Apache Stratos, Magento Commerce Cloud, and OpenShift are some of the other renowned PaaS cloud service models.
Software as a Service
SaaS is a cloud computing model where software is provided as a service over the internet. By accessing software virtually via a web browser, businesses avoid the hassles of buying, installing, and maintaining hardware, freeing up resources. SaaS applications are hosted on the servers of the providers, who manage performance, availability, security, and access.
How Does SaaS Work?
In SaaS cloud service models users share the same infrastructure and application, with the data, made isolated and secure. It comes with safety features like multi-factor authentication and single sign-on which guarantee safe access.
Providers regularly update the software and add new features, ensuring that consumers always have the most recent version without having to upgrade manually. This is done using continuous integration and deployment pipelines.
Additionally, SaaS apps offer APIs to enable integration with other tools and services, facilitating seamless data transfer and automating workflows. Lastly, by relying on global data centers, they guarantee low latency to end-users.
When to Choose SaaS?
SaaS cloud service models become the best choice for brands looking for ready-to-use software solutions that can be quickly deployed without the hassles of in-house development.
These models are perfect for startups and enterprises of all sizes with limited funds as they do not require extensive software infrastructure or maintenance. SaaS apps also help companies with global and remote teams since they foster easy collaboration and access.
Benefits and Limitations
You should take into account the following advantages and restrictions of PaaS cloud service models.
| Pros | Cons |
| Cost efficiency: Requires lower upfront costs on hardware or software as services are provided on a subscription-based model. This also means businesses require reduced staff, which helps cut costs. | Internet reliance: Since the software is provided virtually, service quality depends on internet connectivity and bandwidth. |
| Time efficiency: SaaS solutions are easy to set up, and updates and upkeep are managed by the provider, reducing downtime and workload overhead. This frees up the team to focus on ideation and innovation. | Limited customization: They may not provide the degree of customization needed by some applications, especially for configuring middleware or the underlying infrastructure. |
|
Scalability: Services can easily be scaled up or down to accommodate changing demands during peak seasons or growth phases. |
Data security: With the data being stored off-premises with a third-party provider, data privacy can be a concern. |
|
Free trials: Most SaaS providers offer free trials and slashed subscription fees for new users, which allows businesses to test the waters to check for workflow alignment. |
Performance bugs: During peak hours, performance may occasionally be impacted as SaaS operates on a multi-tenant model. |
|
Fosters collaboration: SaaS solutions come with built-in integration and communication tools like shared workspaces, real-time editing, and more, which enhances team collaboration. |
Vendor lock-in: Migrating workflows from one SaaS vendor to another proves tricky as data gets stored in proprietary formats. |
Leading SaaS Providers
Google Workspace: Formerly known as G Suite, it includes Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Drive, and Meet. Its user-friendly setup, expansive storage, and real-time collaborative capabilities, powered by Google’s search technology, make it second to none across industries.
Microsoft 365: It has over the years, proved itself as the most indispensable suite of tools for businesses. It includes Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Teams, and Outlook. It offers users a unified platform for real-time co-authoring for seamless operations.
Zoom: As remote working grew popular in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, Zoom became an industry leader in video-conferencing services. Its ability to host large meetings without compromising on quality, as well as its unique features such as breakout rooms for smaller discussions, makes it the preferred choice for most businesses.
Slack: It features an intuitive interface that comes with organized channels for easy communication. Additionally, it has vast integration capabilities for tools like Trello which makes it a handy staple for many organizations.
Salesforce: It has made a name in the industry for its resilient CRM platform. Its biggest selling point is its integration capabilities and AppExchange marketplace that allow businesses to leverage third-party apps. Additionally, it boasts a customizable dashboard and AI-powered insights via Salesforce Einstein.
Adobe Creative Cloud, BigCommerce, Dropbox, ZenDesk, Cisco WebEx, and GoToMeeting are some of the other tech giants that offer SaaS services.
Choosing the Right Model Cloud Service Model: A Comparison
Selecting the right cloud service model is crucial to seamless operations, maintaining competitiveness, and accommodating demand fluctuations. So, make an informed decision after considering the following factors.
| Parameters | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Components managed by the provider | Cloud-based storage, servers, networking | Virtual storage, servers, networking, runtime, OS, and middleware | Cloud Storage, servers, networking, runtime, OS, middleware, and applications |
| Components managed by users | Data, applications, OS, middleware, and runtime | Only data and applications | None |
| Pricing structure | Pay-as-you-go for the resources used | For resources used or platform subscription | Subscription basis per user or usage |
| Scalability and customization | High. Resources can be scaled up or down as per workload | Medium. Applications can be scaled up or down within the platform | Limited. Only the application provided can be scaled |
| Integration | High flexible. Integrates seamlessly with various tools and services | Capabilities restricted to within the platform and some external services | Limited to the integration features of the application provided |
| Security | Provider guarantees the physical security of the infrastructure. Users responsible for data and application security | Provider guarantees the physical security of the infrastructure and platform. Users responsible for data and application security | Providers guarantee end-to-end security |
| Compliance | Users are solely responsible although providers may offer compliance certifications | Providers provide compliance with industry standards. Users must check if applications align | Providers offer compliance with standard regulations. Users must check if data and usage comply |
| Support | Basic infrastructure support. Advanced technical support comes with additional costs | Support for platform and application deployment bugs | End-to-end support |
| Disaster recovery | Users are solely responsible although providers may offer backup solutions | Providers typically offer integrated recovery features but users must manage recovery within applications | Comes with built-in disaster recovery options |
| Used by | Typically used by IT administrators, network architects, and developers | Utilized by app developers, start-ups, and DevOps teams | Usually by end-users and small businesses |
| Training needed | High technical knowledge is required | Basic knowledge suffices | Requires no technical familiarity |
Ultimately, your existing infrastructure, workloads, and desired business outcomes will determine your choice of cloud service model.



Unsure which cloud service model will suit your business needs? Schedule a free consultation!
Wrapping Up!
Cloud service models have transformed how businesses handle workloads. IaaS offers flexibility for hosting custom applications and managing storage, while PaaS takes it a step further by taking care of system administration, which frees up your developers to focus on coding. SaaS, on the other hand, delivers ready-to-use services tailored to specific business needs.
As brands leverage cloud-based service models to maximize growth, global expenditure on public cloud setups hence is expected to reach an astounding $72,923 million for IaaS, $176,493 million for PaaS, and $243,991 for SaaS, by 2024,
These numbers speak for themselves arguing the indispensability of cloud service models in today’s market. However, choosing the right cloud service model is key to reaping maximum benefits. We hope our checklist of essential parameters will prove handy in this regard.
But, if you find yourself unsure, consult with cloud experts to make the best pick.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the three main cloud computing service models?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three primary cloud computing service models, each offering unique capabilities that make it suitable for specific business objectives. Cloud service providers nowadays also offer Everything as a Service (XaaS) and Function as a Service (FaaS).
2. How do cloud service models help my business?
Cloud service models empower your business with agility, resilience, and cost efficiency. It encourages innovation and accelerates time-to-market by enabling experimentation and rapid deployment of new services. Simply put, it offers you the adaptability and flexibility needed to thrive with changing market trends.
3. What factors should you consider when picking cloud-based service models for your business?
When deciding on cloud-based service models, look for flexible pricing models, robust data encryption protocols, built-in integration features, and collaborative tools that reduce downtime for business continuity. Lastly, select a tool that complies with industry regulatory standards.
Project Delivery Head
Nitin has over 20 years of IT experience and 3+ years of experience in on-site work in Arizona, USA. In all these years, he has held the positions of delivery manager, module lead, and senior consultant. Expert in advocating product life cycle phases while using self-motivational skills and problem-solving abilities. He works on the principle of “Always Deliver More than Expected.”