Data breaches, cyber-attacks, and malware intrusion have become standard terms in today’s IT sector. To tackle these online threats, developers follow front end security best practices.
With a data breach costing USD 4.35 million (on average) globally, it is crucial to implement definite, practical measures.
Now, you might think a secure front end practice is quite technical.
Well, in short, yes, it is. However, some solutions don’t require the knowledge of intricate coding. In fact, you can follow some simple front end development best practices and secure your digital asset.
Without any ado, take a look at proven web development security best practices that can secure your online product profoundly.
Most Common Front-end Vulnerabilities
Before jumping right to the best practices, it is vital to acquaint yourself with the most prominent web-based cyber attacks. Here are the most common attacks to watch out for:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): This attack injects malicious scripts into trusted websites. When a user visits the website, their browser unknowingly executes the script, stealing data and redirecting them to malicious sites
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): In this cyber attack, attackers trick a user’s browser into performing unauthorized actions on a trusted site. Imagine clicking a link that unknowingly transfers money out of your bank account – that’s CSRF
- Clickjacking: This attack involves layering a transparent overlay on a legitimate site. When a user clicks what seems like a button on the trusted site, they’re actually clicking a malicious button hidden beneath. Phishing emails use clickjacking techniques
- Injections: These attacks involve slipping malicious code into user inputs like forms or search bars. This code can steal data, manipulate content, or take control of the web application
- Insecure Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs deliver content like images or scripts to websites. If unsecured, attackers can tamper with CDN content, injecting malicious code into legitimate websites
By understanding these vulnerabilities, you can take steps to secure your front-end and protect your users.
Front-End Security Risks and Best Practices to Prevent Them
In this section, we will explain each cyber risk and the direct solution to prevent them. So, scroll ahead to understand some valuable pointers.
Input Validation and Data Sanitization
What do these terms mean?
- Input validation: Ensures proper data enters the workflow in an information system
- Data sanitization: Remove flawed data permanently to make it unrecoverable
Such front end security best practices ensure protection against cyber threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Best Front End Practice and Solutions
Developers can perform these web security best practices or frontend practice on both the server and client end.
Here are the standard and actionable solutions:
- Check for good inputs (perform whitelisting of data)
- Validate and sanitize user input before processing
- Utilize reputed libraries to sanitize data
Overall, these steps help ensure that your input is free from malicious code.
Protection from Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
An XSS attack includes injecting a malicious script into an application’s or website’s code. The attacker can use any client-side language to perform this action.
What happens after a successful XSS attack?
Here are some scenarios:
- The user redirects to a malicious website
- The web browser crashes unexpectedly
- The attacker obtains the end user’s cookie information
- Some cyber criminals can capture your keystrokes
Moreover, cross-site scripting is a common cyber threat that developers can prevent by following front end security best practices.
Frontend Practice Solution
Specific strategies can prevent XSS attacks. These include the following:
- Encode content that a user generates before rendering on the page
- Don’t load external scripts from doubtful sites
- Install multiple walls to protect the website from malicious attacks
- Perform output encoding to prevent common vulnerabilities
You can prevent most XSS attacks after following such front end or web development security best practices.
Safeguarding Data Authentication
Authentication is a process. It includes verifying a user’s identity. Websites or apps allow access to information after successful data authentication.
There are proven ways to implement a frontend practice that secures authorization and authentication. Hiring dedicated developers will always ensure adherence to frontend logging best practices.
However, you can test some of the solutions yourself for protecting data.
Solutions for the Best Front End Practice
To prevent unauthorized access and safeguard data, you can follow these practices:
- Use JSON web tokens (JWT) that encode user information
- Enable multi-factor authentication
- Enforce strong password policies and multi-stage verification
- Always use HTTPS for data encryption
- Implement cross-origin resource-sharing headers
- Use attribute-oriented access control
All in all, these front end or web development security best practices can improve your data safety profoundly.
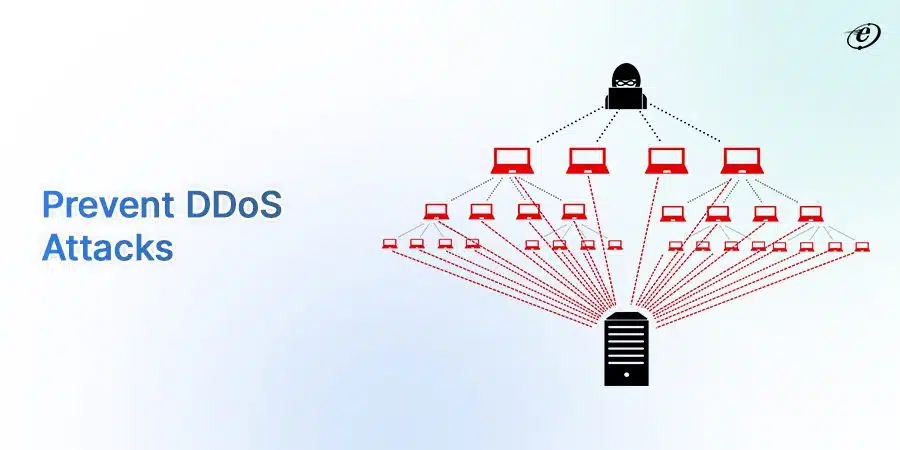
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack Protection
A DDoS attack can make a website inaccessible to a user. How?
In this cyber attack, the culprit floods your server with internet traffic. As a result, this overwhelming traffic blocks an authentic user from exploring your website.
Here’s how you identify such attacks:
- You have traffic from similar user profiles
- There is an unprecedented surge in single-page requests
- You notice an artificial spike in the online traffic
- The traffic increases from a specific IP range
Don’t worry. You can prevent such attacks by following specific front end development best practices.
Front End Practice DDoS Solutions
Follow these tips to prevent distributed denial of service attacks:
- Use a content delivery network (CDN)
- Create a blackhole route and direct traffic towards it
- Implement rate limiting
- Put web application firewall between internet and server
Such front end security best practices need proper inclusion in your online safety strategy.
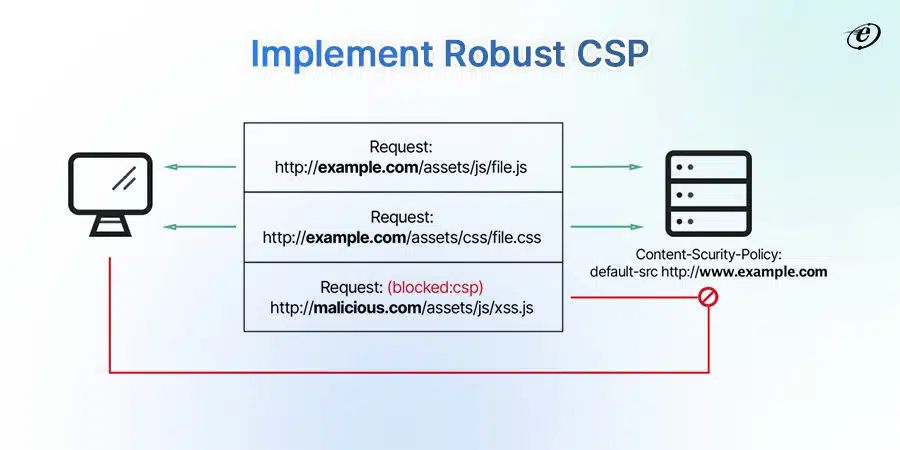
Establish a Content Security Policy (CSP)
In simple words, CSP is a security framework or standard. It is a front end practice to prevent code injection attacks. You can also mitigate XSS threats or clickjacking.
If you are wondering about the term ‘clickjacking,’ here is its meaning:
Clickjacking means fooling users into thinking they are clicking on a specific site. But the action redirects them to another location.
So, is CSP a good frontend practice?
In a word, yes. It decreases the ability of an attacker to perform a cross-site scripting attack. Scroll ahead to know the front end security best practices using CSP.
How to Implement CSP
Follow these tips to implement a content security policy the right way:
- Specify domain and content directives
- Add an HTTP header to the web server
- Run CSP in report mode for better analysis
- Disable inline JavaScript and allow HTTPS connections
If you feel such front end development best practices are too technical, approach a reliable IT firm for guidance. Sometimes, you can even get help from active online developer communities.
Install Dynamic Application Security Testing Scanner
The short form of Dynamic Application Security Testing is DAST.
It is a scanner that detects vulnerabilities in a web application. Developers use this front end practice by planning simulated attacks.
Notably, such front end security best practices don’t require access to the source code. It is, however, vital to note that DAST scanning can be time-consuming.
Frontend Practice DAST Solution
Generally, skilled developers can implement a DAST scanner in the development life cycle. This way, it is possible to detect vulnerabilities in an early stage.
You can prevent the following cyber threats after implementing this front end practice:
- Cross-site scripting
- SQL injection
- Configuration error
- Encryption issues
Ensure that you use the DAST scanner during runtime. Such web security best practices can prove highly invaluable.
Audit Node Package Manager (NPM)
Node Package Manager is a library for JavaScript software packages. Some popular front end security best practices include auditing these packages.
The impact of this frontend practice is as follows:
- Identify potential vulnerabilities
- Provide suitable patch suggestion
You need to know about running simple commands to implement such front end development best practices.
Solution for This Front End Practice
To audit NPM packages, follow these steps:
- Type ‘npm audit’ and hit enter
- Assess the report of the audit
- Run suggested commands
Ensure that the JavaScript package has files like package.json and package-lock.json.
Follow Front End Security Best Practices from Today!
Front-end security best practices can profoundly safeguard your web application or site. These seven strategies can prevent several cyber attacks, thereby maintaining the top functioning of your digital asset.
Focus on input validation to prevent cross-site scripting attacks and DDoS threats by implementing such front end practice solutions. Notably, most of these front end development best practices are simple to implement.
If you don’t have a technical team, fret not. Contact us and receive all-inclusive guidance on reliable frontend logging best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the meaning of front end security?
Front end security is the process of safeguarding websites or applications from typical cyber-attacks. Developers follow well-known front end security best practices to secure user data and maintain good health of a site, portal, or mobile application.
2. What are the types of security controls in front end practice?
Three ways to perform front end development best practices are through management, physical, and operational security controls.
3. What are management security controls in frontend practice?
Management security controls include the process of implementing a fully secure frontend environment. Popular as administrative controls, these measures ensure that your stakeholders follow relevant policies to prevent cyber threats.
4. What is the meaning of physical security?
Physical security implies the protection of data, hardware, and business assets. This security control doesn’t fall directly into front end security best practices. However, it is vital for securing IT infrastructure through surveillance, environment control, and contingency planning.
Excellence-driven professional with 15+ years of experience in increasing productivity, and revenue, while effectively managing products of all sizes. He has worked for international clients in the US, UK, and Singapore and local companies in various domains. With excellent attention to detail and a methodical approach to execution, he is an expert in bringing projects to a successful stage. He follows James Humes’s famous saying- “The art of communication is the language of leadership.”