Overview: UX and UI design are two interdependent roles in creating digital products. UX focuses on the structure and functionality, while UI enhances the visual appeal and interactivity. Together, they ensure seamless and engaging user experiences. This blog covers a detailed comparison of UX vs UI. It will help you understand these two roles and guide you in deciding which type of designer to hire for your next project.
In the world of design, two key roles often come up in conversation: User Experience (UX) designers and User Interface (UI) designers. While these roles are distinct, they are deeply interconnected and equally vital to creating effective digital products.
Let’s take a simple example to understand these terms:
Building a hotel mirrors the collaboration between UX and UI designers.
You must be thinking, how?
The architect (like the UX designer) plans the purpose, structure, and guest journey, ensuring a seamless experience. The interior designer (like the UI designer) enhances the hotel’s look, feel, and functionality, aligning decor and usability with the intended design. Together, they ensure the hotel is both practical and inviting. Similarly, UX focuses on the product’s overall experience, while UI perfects its visual and functional interface, creating harmony and usability.
A recent study reveals that a well-designed UI can boost conversion rates by up to 200%, while an exceptional UX can increase them by 400%. Additionally, 83% of users favor visually appealing and modern websites, highlighting how effective UI vs UX design can significantly enhance business performance and user engagement.
This blog will examine the roles of UX vs UI designers, their responsibilities, and how they work together to create intuitive and engaging user experiences. If you’re still unclear about the concepts of UI and UX, we’ll start covering the fundamentals to help clarify any doubts you may have.
Transform your ideas into stunning designs! Hire a skilled UI/UX designer today to elevate your user experience.
What is UI?
Humans connect with technology through the user interface. The user’s digital experience is shaped by it as it focuses on how a user uses visual and audio components, including typefaces, buttons, animations, sounds, and icons, to engage with an application or website. For example, display screens, keyboards, mouse, etc.
A well-designed user interface conveys the company’s identity and values and improves usability. Button, icons, menus, navigation, and gesture controls are just a few of the characteristics that skilled UI designers use to create intuitive communication.
Leading app development companies employ designers who can produce user-friendly and engaging interfaces. They design aesthetically pleasing interfaces that align with brand guidelines.
Find the latest UI design trends.
Here are a few examples of UI in action
- Choosing a professional color scheme and clean typography to reflect the brand’s identity.
- Designing intuitive icons and interactive buttons for easy navigation.
- Ensuring the interface is responsive and visually consistent across devices.
Key Elements of a User Interface
| Element | Description |
| Input Control | Users can enter data into the system through input controls. You have utilized input controls if you click on a checkout page and enter your credit card information. |
| Navigation Components | You’re using navigational user interface elements while you’re switching between pages. A hamburger menu on an Android device and tab bars on an iOS device are common navigational elements. |
| Containers | Containers link things together for better organization and to create logical flows in the user interface, much like the boxes you use to store seasonal decorations. For instance, cards, tables, accordions, etc. |
| Informational Components | The informational component of UI refers to presenting relevant data and content, such as text, images, or notifications, that help users understand, navigate, and make informed decisions within the interface. For example, text, progressbar, tooltips, etc. |
| Images/Graphics | Images and videos in UI design serve aesthetic and informational roles, enhancing user engagement, providing context, and improving the overall experience with visual elements like photos, illustrations, and animations. |
| Icons | Icons are easily recognizable UI elements, like pause and play symbols, that enhance the visual appeal of a design while providing users with intuitive ways to interact and navigate the interface. |
| Forms/Input Fields | Input fields in UI designs allow users to enter text, such as on login and sign-up pages for gathering information or in search bars for finding specific content. |
| Buttons | Buttons are interactive UI elements users click to trigger actions or submit forms. With customizable shapes and diverse CTA text options, they are among the most commonly used elements in UI design. |
| Output Elements | Output elements display results based on user inputs, including alerts, warnings, success, and error messages. They are not neutral; they depend on user interactions and operations to convey relevant information or feedback. |
Demystifying UI/UX for Web Designers
What Does a UI Designer Do? Roles and Responsibilities Explained
UI designers are responsible for creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces for applications, websites, or software. Their tasks include wireframing, prototyping, designing layouts, choosing color schemes, and ensuring consistency across platforms. They also handle competitor analysis, design guidelines, and testing to enhance usability and user engagement. Let’s uncover all the responsibilities of a skilled UI designer.
-
Wireframing & Prototyping
Wireframes, which are simple sketches or blueprints of the user interface, are the first step in the design process for UI designers. These wireframes show the product’s framework but exclude the finished design components. On the other hand, prototyping allows UI designers to test and refine visual designs by showcasing interactions. There are three types: low-fidelity wireframes, clickable prototypes, and high-fidelity prototypes.
-
Collaboration with UX Designer
UI designers collaborate with UX designers to ensure usable and visually appealing products. While UX focuses on user journeys, UI designs the interface and interactions. UI designers use user research and personas provided by UX, then create designs based on wireframes. Clear communication and collaboration with web developers and teams are essential for successful project completion.
-
Keeping Up with Design Trends
UI designers stay current with tools and trends to provide cutting-edge, competitive designs. They make wireframes, choose colors and fonts, design screens and UI elements, specify interactivity, and guarantee consistent, responsive user experiences. UI design is a field that is constantly changing. Therefore, designers must stay updated with the latest design trends, technologies, and tools. As a result, the product remains competitive and modern by allowing them to include new features and advancements in their designs.
How will 2025 shape UI design trends for the next decade?
Don’t settle for average—hire a skilled designer today and turn your vision into an exceptional user experience.
-
Testing & Iteration
UI designers are involved in user testing, gathering feedback, and making design improvements based on user interactions. This iterative process helps refine the design and fix usability, functionality, or visual appeal issues. User feedback is often used to enhance the interface further.
-
Choosing Color Schemes and Typography
A UI designer is responsible for selecting color palettes and fonts that align with the brand identity and create a visually cohesive design. Choosing colors and typography is crucial, affecting readability, user emotions, and overall product perception. UI designers often ensure accessibility by considering color contrast and font legibility for users with disabilities.
-
Responsive Design
UI designers have to make sure that their designs are responsive. This entails developing user interfaces that adjust to various screen sizes and resolutions on mobile devices, tablets, and PCs. A skilled user interface designer must guarantee that the interface is both aesthetically pleasing and usable on all platforms.
How important is it to find a responsive web design company?
What is UX?
The process of determining and comprehending end users’ needs, followed by creating a workable solution, is called UX design. It basically involves the design of the complete acquisition and integration process, encompassing elements of branding, design, usability, and functionality. From digital experiences to tangible goods, UX design ensures that every user’s engagement with a product is satisfying.
UX design is essential to the success of any product or service in the current digital era. It emphasizes a product’s usability and functioning and creates a smooth and engaging user experience. Strong UX increases customer loyalty and propels company expansion.
Examples of UX in Action
Let’s consider a mobile banking app development where the following tasks need to be done by a UX designer:
- Conducting user research to identify the most commonly used features.
- Designing a simple navigation flow for quick access to account balances and transactions.
- Testing the app’s usability to ensure it meets user expectations.
Key Elements of User Experience
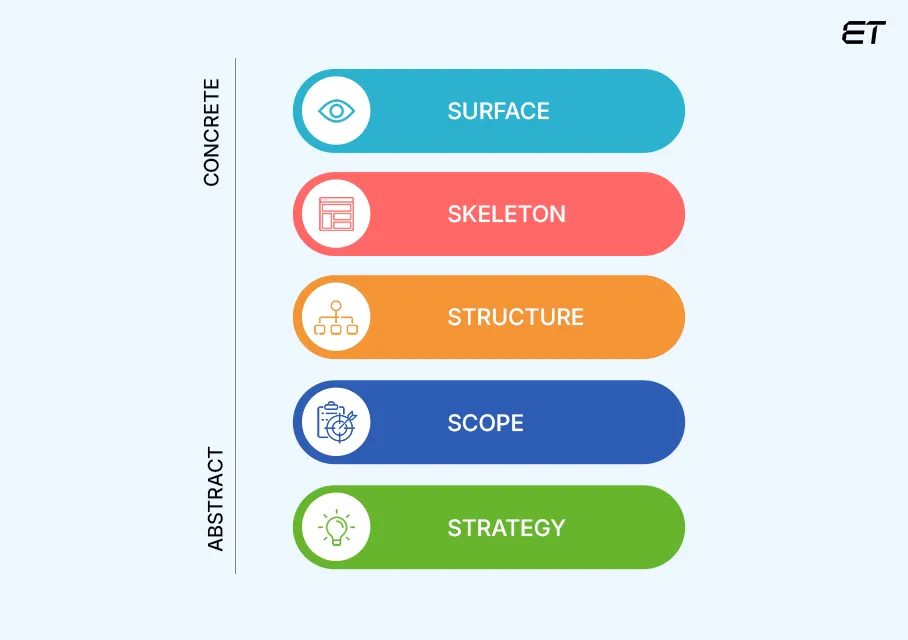
The five key elements of UX—strategy, scope, structure, skeleton, and surface—form the foundation of Jesse James Garrett’s “Elements of User Experience” framework. These elements guide the design process to ensure a user-centered and effective product. Here’s an explanation of each:
Image 10
-
Strategy
The strategy phase establishes the foundation by aligning user needs and business goals. UX designers conduct research to understand users, their pain points, and objectives. For example, building an app for electric car charging requires addressing product goals (e.g., locating stations) and user needs (e.g., directions, availability, and pricing) to ensure a meaningful solution.
-
Scope
The scoping phase establishes the features and substance of the product. Features and functionalities that must be introduced are referred to as functional requirements. The theme, photos, sounds, and videos that will contribute to adding value and meeting standards are outlined in the content requirements.
In our example, content requirements include things like charger data, station photos, and maps, while functional requirements outline capabilities like the ability to save preferred charging stations. These specifications ensure the product meets user needs and aligns with strategic goals, effectively guiding the design and development process.
-
Structure
The structure phase organizes the design and defines user interactions with the product. It consists of:
- Interaction Design: Builds on functional requirements to define how users interact with the system and how it responds, including handling errors. Conceptual models, like flowcharts, detail user actions and system reactions.
- Information Architecture: Builds on content requirements to structure information, ensuring users can find what they need. Site maps outline content hierarchy and navigation.
For an electric car charger app, the structure could include a homepage for location input, leading to a list of stations with links to individual details. User flows might show responses to inputs, including handling errors or displaying nearby station results.
Front-end architecture and its significance for businesses.
-
Skeleton
The skeleton layer focuses on the visual layout and flow of information. UX designers create wireframes to arrange navigation, buttons, images, and text, ensuring smooth user movement and clarity of interactive elements. For an electric car charger app, wireframes include a header with navigation, a station image, a map link, and station details, as well as visually organizing functionality and content for intuitive user interaction.
-
Surface
The surface layer finalizes the product’s visuals, focusing on layout, typography, styling, and colors. Wireframes guide the creation of visually appealing and navigable pages. For an electric car charging app, this could involve a consistent color palette, prominent placement of key information, and a clear layout with a logo at the top, ensuring a cohesive design and intuitive user experience.
Why are UX design principles important in planning front-end development?
What Does a UX Designer Do? Roles and Responsibilities Explained
User Experience (UX) design has become a cornerstone of creating successful digital products. But what exactly does a UX designer do? Let’s break down their roles and responsibilities to understand their critical contributions better.
-
Conduct User Research
Find out the issue they are attempting to resolve for the user and how it fits the enterprise brand’s objectives. They use usability testing, surveys, and interviews to learn about user demands, behaviors, and pain areas. Besides this, they create journey maps and user personas to inform design choices. A/B testing, focus groups, surveys, and one-on-one interviews are some examples of user research tools.
-
Create User Persona & Scenario
UX designers create user personas from your research to identify key product and service elements. Begin mapping the user flow to visualize each step users take, ensuring the design aligns with their needs and enhances the overall experience.
-
Design
During the design phase, UX designers create site maps, wireframes, and prototypes to visualize the final product. Wireframes outline basic layouts, while prototypes simulate interactions for testing. Finally, focus on visual design, refining color schemes, typography, and aesthetics to craft a polished and visually appealing product.
-
Information Architecture
UX designers organize and structure content to ensure seamless navigation and understanding. This involves creating clear site maps and content hierarchies, enabling users to quickly locate information and achieve their goals efficiently while interacting with the product or service.
-
Conduct User Testing
UX designers employ usability testing, which monitors how actual people interact with the product or service to confirm the design. They determine whether there are any design flaws and create fixes.
-
Collaborate with Teams
UX designers collaborate with dedicated developers, product managers, marketers, and other designers to ensure designs align with business goals, maintain brand consistency, and incorporate feedback. Clear communication and teamwork are essential to translating design concepts into functional, user-friendly products while ensuring consistency and feasibility throughout development.
Meet the Professional UX Designers to create visually stunning, user-friendly interfaces tailored to your audience.
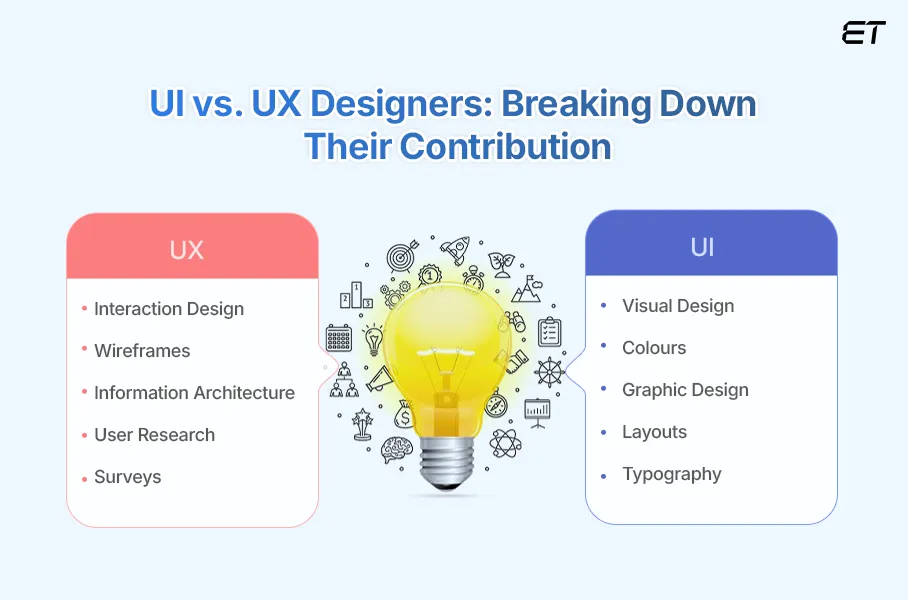
UI vs. UX Designers: Who Does What in Digital Design?
UI and UX designers play distinct yet complementary roles in digital design. Together, they create seamless, satisfying user experiences that meet both user needs and business goals, highlighting the importance of collaboration in delivering exceptional digital products. But everyone like you is confused about which role out of UI vs UX designer is crucial for your dream project. Let’s go ahead and find the answer right away!
UX vs UI Designers: Skills Required
To excel in their role, UI designers require a combination of technical expertise, creativity, and a deep understanding of user needs. Here are the essential skills every UI designer should possess:
| UI Designer Skills | Explanation |
| Prototyping | Prototyping and interaction design are vital for UI designers, enabling them to create engaging interfaces, ensure intuitive interactions, iterate efficiently, validate concepts with users, and collaborate effectively with development teams for seamless user experiences. |
| Responsive Design | Understanding responsive design concepts, such as scalable components and adaptable layouts, is crucial for producing a consistent user experience. Knowledge of design systems such as Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines or Google’s Material Design guarantees consistency and scalability across designs. |
| Intuitive Interface Design | UI designers must prioritize intuitive design, blending user behavior insights with seamless aesthetics to create engaging, efficient experiences that captivate users with minimal learning curves and maximize usability. |
| Exploration and Iteration | UI design is iterative, requiring creativity to experiment with layouts, colors, and interactions, refine concepts, and improve designs based on testing and feedback. |
| Basic Coding Knowledge | For UI designers, knowledge of front-end technology is equally crucial. Although writing production code is not required, knowledge of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular enables UI designers to interact with developers and assess the viability of their ideas. |
| Collaboration & Communication Skills | UI designers must excel in teamwork, communication, and empathy to collaborate with UX designers, developers, and stakeholders. Strong written skills support negotiation, documentation, and feedback, enabling cohesive designs aligned with user needs and corporate objectives for successful outcomes. |
| User-Centered Problem Solving | Empathy and user-centric problem-solving are crucial for UI designers. By understanding user needs and challenges, designers create functional, enjoyable products that solve real problems, enhancing both the experience and purpose of the product. |
| Attention to Details | Attention to detail is crucial for UI design, ensuring spacing, alignment, and consistency. It reflects the ability to refine critical elements, make informed decisions, and maintain a cohesive, polished interface through effective organization and time management. |
Out of UI vs UX, UX designers need a blend of research, design, testing, and collaboration skills to create user-centric products that provide a positive and efficient experience. Several key skills are essential for a UX designer to excel. Let’s uncover all of them:
| UX Designer Skills | Explanation |
| User Research | Surveys, interviews, and usability testing are some of the methods used by UX designers to collect data on user needs, preferences, and behaviors to inform decisions regarding design. |
| User Testing | Real-world user testing enables designers to pinpoint usability problems, pain points, and areas in need of development. To make sure it lives up to user expectations, they use this feedback to improve the user experience and iterate on designs. |
| UX writing | UX designers must improve UX writing to create clear, concise, and engaging content that guides users effectively. Well-crafted microcopy enhances navigation, reduces frustration, and boosts overall user satisfaction, making the product more intuitive and enjoyable. |
| Information Architecture | Information architecture is the process of arranging data in a way that makes sense. UX designers must plan out the categorization of information and make sure that logical navigation and an intuitive layout allow people to discover what they need quickly. |
| Front end development | While UX designers aren’t required to code, basic knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript enhances collaboration with developers, sets realistic design expectations, and improves marketability, especially in startups or when transitioning to UX engineering or development. |
| Problem-Solving Abilities | A successful UX designer uses critical thinking, creativity, and empathy to uncover user insights and create user-centered solutions that solve real-world problems, enhancing overall usability and the user experience. |
| Adaptability and continuous learning | UX designers must stay updated with evolving technologies, design trends, and user expectations. Continuously learning and adapting to new tools and industry standards helps them deliver innovative experiences and remain competitive. |
| Prioritization and time management | Time management is crucial for UX designers to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and stay productive. It involves planning, goal setting, and organizing tasks to avoid distractions to prevent burnout, and ensure efficient project completion. |
| Agile | Agile UX design blends Agile project management with UX design, using iterative processes to build products. While it is not essential for UX designers to master project management, understanding the basics can help in robust UX development. |
UX vs UI Designer: Tools Knowledge
As technology develops, designers need to stay updated with the newest tools and applications. Technical abilities include knowing how to use front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to develop designs and being proficient with design software like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma.
Although UX vs UI designers focus on separate areas of the design process, UX and UI design are closely intertwined, reflected in the tools they employ. While both roles may use overlapping tools like Figma, the focus of each designer’s toolset varies significantly.
UX designers focus on the overall user experience, including research, user flow, and testing. Key tools for UX designers include:
| Research and Testing | Tools like UserTesting, Hotjar, and Lookback are used for gathering user feedback, conducting usability tests, and analyzing behavior. |
| Wireframing | Balsamiq and Wireframe.cc are commonly used for creating low-fidelity wireframes to outline structure and user flow. |
| Prototyping | Axure and Figma allow for creating interactive prototypes to simulate user interactions. |
| Analytics | Google Analytics and Crazy Egg help track user behavior to improve designs based on data. |
Out of UX vs UI, UI designers concentrate on the look and feel of the product, creating the visual elements users interact with. Common tools for UI designers include:
| Design | Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD are used to create high-fidelity designs and detailed user interfaces. |
| Graphics | Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator are essential for crafting visual elements such as icons and images. |
| Collaboration and Handoff | Tools like Zeplin and InVision streamline collaboration between designers and developers by sharing assets and design specifications. |
UX vs UI Designers: Focus
While UX and UI design work together, but out of UI vs UX , UX focuses on usability and flow, while UI focuses on visual appeal and interaction.
| UX Focus | UI Focus |
| When a user interacts with the product overall, their feelings and emotions | The way a thing feels and looks and what it communicates to users |
UX design, also known as user experience design, is concerned with how simple, straightforward, and pleasurable a product (such as an app or website) is used. A dedicated UX designer aims to ensure users have a smooth, effective, and enjoyable experience. It entails researching user demands and creating a product’s logical flow and structure. Logic and user-centered design that improve accessibility and satisfaction are at the heart of UX design.
While comparing UX vs UI, the product’s interactive visual components are the main emphasis of UI design. The appearance, feel, and functionality of the interface are all under the control of UI designers. They guarantee that the design complements the brand, is consistent, and is visually appealing.
UX vs UI Designers: Process
Out of UX vs UI design, UX design focuses on user research, flows, and testing for usability, while UI design emphasizes visual elements, like layout and colors, to create an engaging and functional user interface.
UX vs. UI designers may be sure they are covering all the bases and producing an interface that will be user-friendly and effective by adhering to a clearly defined procedure. Let’s cover all the steps of each one.
UX Design Processes
| STEP 1 | Define | Create user personas and map out user journeys to clarify pain points and opportunities. |
| STEP 2 | Research | Understand user needs, behaviors, and goals through interviews, surveys, and data analysis. |
| STEP 3 | Analysis & Planning | Brainstorm ideas and solutions to meet user needs and business goals. |
| STEP 4 | Design | Design low-fidelity wireframes to outline basic layout and functionality. |
| STEP 5 | Prototyping | Develop interactive, high-fidelity prototypes for testing and refinement. |
| STEP 6 | Testing | Conduct usability tests with real users to identify issues and gather feedback. |
| STEP 7 | Implement | Work closely with developers to ensure the design is executed accurately. |
| STEP 8 | Evaluate | Continuously monitor user feedback and analytics to make further improvements. |
UI Design Processes
| STEP 1 | User Research | Understand the target audience, business goals, and competitor products to guide the design direction. |
| STEP 2 | Define Objective | Translate user research into design objectives, defining key features and tasks while focusing on the target audience. |
| STEP 3 | Wireframing | Create basic layouts and structures without visual details to outline the placement of elements. |
| STEP 4 | Visual Design | Apply colors, typography, and branding to create high-fidelity mockups that reflect the final look. |
| STEP 5 | Prototyping | Build interactive prototypes to simulate user interactions and visualize the design in action. |
| STEP 6 | Usability Testing | Test prototypes with real users to identify any usability or visual issues. |
| STEP 7 | Hand Off | Deliver the finalized design to developers with assets, specifications, and guidance for implementation |
UX vs UI Designers: Objective
A UX research objective defines the purpose of the study, guiding the research direction and method selection. Understanding user demands, behaviors, and pain spots is one of the goals of UX research in order to guide design choices. UX analysts seek to determine the objectives and difficulties of users by obtaining information using techniques such as surveys, user interviews, and usability testing.
The UX designers follow the SMART framework, which stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. During the design and development stages, this framework directs UX efforts and aids in determining success.
All in all, we can say that UX research seeks to enhance the user experience by making the product more effective, fulfilling, and in line with the requirements and expectations of the target audience.
While comparing UX vs UI, a UI designer’s objective is to create an aesthetically pleasing and functional user interface that enhances the overall user experience.
Their objective is to create user interfaces that are consistent with the company’s brand, visually appealing, and simple to use. To guarantee a flawless experience, they concentrate on components like layout, typography, color schemes, iconography, and interactivity.
UI designers are responsible for designing all the screens a user will navigate and creating the visual components and their interaction features that make this movement possible. In addition to being aesthetically pleasing, UI designers strive to ensure that the product is simple to use and intuitive. Their goal is to blend usability and aesthetics such that the interface complements the product’s functionality and user objectives.
UX vs UI Designers: Deliverables
Deliverables are tangible outputs created during the design process, such as wireframes, mockups, and prototypes. UX and UI designers need them to communicate ideas clearly, gather feedback, guide development, and ensure consistency, ultimately aligning design with user and business goals.
UI design deliverables are tangible outputs created throughout the design process to communicate ideas, gather feedback, and guide development. These deliverables help ensure clear communication between designers, stakeholders, and developers throughout the design process. Key UI design deliverables include:
UI Designers Deliverables
| User Research Reports | Detailed findings from user interviews, surveys, or focus groups highlight user needs, pain points, and behaviors. |
| Personas | Fictional representations of user segments based on research data help to guide design decisions. |
| User Journeys | Diagrams illustrate the steps users take to complete tasks, identifying key touchpoints and opportunities for improvement. |
| Design Handoff | A design handoff includes mockups, interactions, specs, and assets for developers to implement the design. Designers should collaborate with developers early to ensure feasibility within project timelines and budgets. |
| Mockups | Mockups are full-size models showcasing design functionality and visual appeal. They help developers, stakeholders, and clients assess the design, aid in user testing, and enhance a designer’s portfolio. |
| Icon Sets | Icon sets are collections of symbols that represent functions or content, enhancing usability and visual appeal. They provide clear cues, transcend language barriers, and ensure consistency, aligning with the product’s overall design system. |
| Usability Testing Reports | Insights from testing prototypes with real users, identifying usability issues and areas for improvement. |
If we compare UX vs UI, UX designers also create several key deliverables throughout the design process to communicate findings, decisions, and design concepts. Important UX deliverables include:
UX Designers Deliverables
| Persona | A persona is a fictional representation of typical users, including their goals, motivations and demographics. It helps designers empathize with users and tailor design decisions. |
| Customer Journey Maps | Diagrams that map the steps users take to complete tasks identify pain points. |
| Brainstorming | Brainstorming is a collaborative process where designers generate numerous ideas to address user research findings, including unconventional ones, later narrowing them down to the most promising solutions. |
| Competitive Analysis Report | Competitive analysis involves evaluating competitors to identify strengths and weaknesses. It helps set design direction, focusing on areas for improvement based on competitor insights. |
| Sitemap and Information Architecture | A sitemap organizes a product’s content and information architecture, aiding navigation and usability. It’s a key UX deliverable, evolving with prototypes and user testing for clarity. |
| User Flow | A user flow diagram outlines the steps a user takes within a product to achieve a goal. It helps designers evaluate process efficiency and refine execution, focusing solely on interactions within the product. |
| UX Wireframes | Low-fidelity layouts illustrate the structure and flow of the interface. |
| Interactive Prototypes | Interactive models are used to test user interactions and refine designs. |
The Dynamic Duo: Collaboration Between UX and UI Designers
UX and UI designers collaborate closely throughout the design process to create a seamless, user-friendly, and aesthetically appealing product. Continuous collaboration, testing, and feedback between UX and UI teams help improve design, ensuring it aligns with user needs and performance goals.
A thorough examination of how UI and UX designers work together at every step of the design process can be found below.
1. Research & Discovery
At this point, the UX designer conducts user research to learn more about the target user group and their objectives, problems, and needs. They may develop UX personas based on their research. However, UI designers also take part at this stage to comprehend the technical limitations, visual needs, and brand identity, ensuring the product’s visual design complements its user experience objectives.
2. User Flow & Wireframe
Coming up with potential solutions is the next stage after determining what issue has to be resolved and for whom. At this point, UX designers concentrate on usability and functionality to ensure the website or app satisfies user needs.
UX designers provide wireframes and user flows. User flows describe the steps users take to complete activities in the product, whereas wireframes are low-fidelity designs that specify the arrangement and composition of essential displays. The UI designer is informed about the selected solution and preliminary design concepts during this phase of the product design process, headed by the UX designer.
3. Visual Design & Prototyping
As the project moves into visual design, UI designers take the lead. The UX designer will sketch out initial ideas, define the information architecture for the product, and create basic wireframes and/or low-fidelity prototypes.
During wireframing and information architecture, UX designers focus on creating a logical, user-friendly journey without considering aesthetics, which is the UI designer’s responsibility later. The UX designer ensures the structure is efficient, while UI designers refine the visuals and interactions.
4. Testing & Validating Early Design
With the product blueprint ready, UX designers conduct user testing to ensure the solution addresses user problems and has a logical structure. They evaluate usability, identify pain points, and gather feedback on flows and functionality. UI designers focus on visual appeal and intuitive interactions. Both designing teams collaborate to refine user journeys, interactions, and visual design based on test results, enhancing clarity, usability, and the overall user experience.
5. Launch & Post Launch
The final designs are given to the dedicated developers. The developers will create the final product that the end user will interact with based on the designs and specifications supplied by the UI and UX designers.
UX and UI designers evaluate developers’ work, make necessary adjustments, and do more user testing prior to launch. They ensure correct platform implementation by iterating designs in response to input.
Post-launch, both teams monitor performance, gather feedback, and collaborate on updates to enhance usability and aesthetics. By aligning functionality with visual appeal, they ensure the product meets user needs and goals effectively.
Selecting the Ideal Designer: UI vs. UX for Your Dream Project
The terms UX and UI design are interchangeable most of the time. But there is a thin line of difference between them. A UX designer is responsible for ensuring a product’s overall usability and functionality. On the other hand, a UI designer is responsible for the visual elements of a product—how it looks and feels.
Despite their distinct areas of expertise, both roles are essential to a product’s overall success. That’s why there is always confusion: which one UX vs UI is best for your dream project?
The nature of your ideal project will ultimately determine whether you choose a UI or UX designer. Hire a UX designer if user experience and functionality are your top priorities. Select a UI designer if aesthetics and visual appeal are crucial to you.
Employing a multiskilled designer who can manage the product design process from beginning to end will yield the most thorough outcome. At eLuminous Technologies, we provide experienced designers with a track record of designing aesthetically pleasing designs within your pre-decided budget. Let’s meet and discuss your project!
Frequently Asked Question
What is the difference between UX design and product design?
UX design focuses on crafting seamless, user-centered experiences by improving usability and interaction. Product design encompasses the broader process, including defining features, visual aesthetics, and business goals and balancing user needs with product strategy.
How much does a UI/UX designer cost?
UI/UX designer costs vary by experience, location, and project scope. Freelancers charge $25–$150/hour, while agencies may cost $75–$250/hour. Complex projects or niche expertise increase pricing significantly.
Find the cost to hire UI/UX designers in 2025.
How do I hire a UI/UX designer?
To hire a UI/UX designer, first define your project requirements, write a precise job description, and then look via job boards like Upwork, Dribbble, and LinkedIn to find a UI/UX designer. Examine portfolios, evaluate interviewees’ communication abilities, and ensure they support your goals. Additionally, you can contact IT staff augmentation services, which can assist you in locating the ideal designer to meet the requirements of your project.
Elevate your product’s user experience! Find the perfect UI/UX designer to craft intuitive designs and develop a top-notch front end.

With 9 years of experience in crafting intuitive and engaging user experiences, Trunal is a certified UX professional, holding credentials in Google UX Design Specialization and Accenture’s Digital Skills. Armed with a diploma in Animation, he specializes in transforming user and business needs into visually compelling designs. His expertise spans Visual Design, Wireframing, Interaction Design, Responsive Design, Design Systems, and Rapid Prototyping, along with front-end technologies. Trunal is committed to delivering seamless, user-centric solutions that enhance digital experiences.